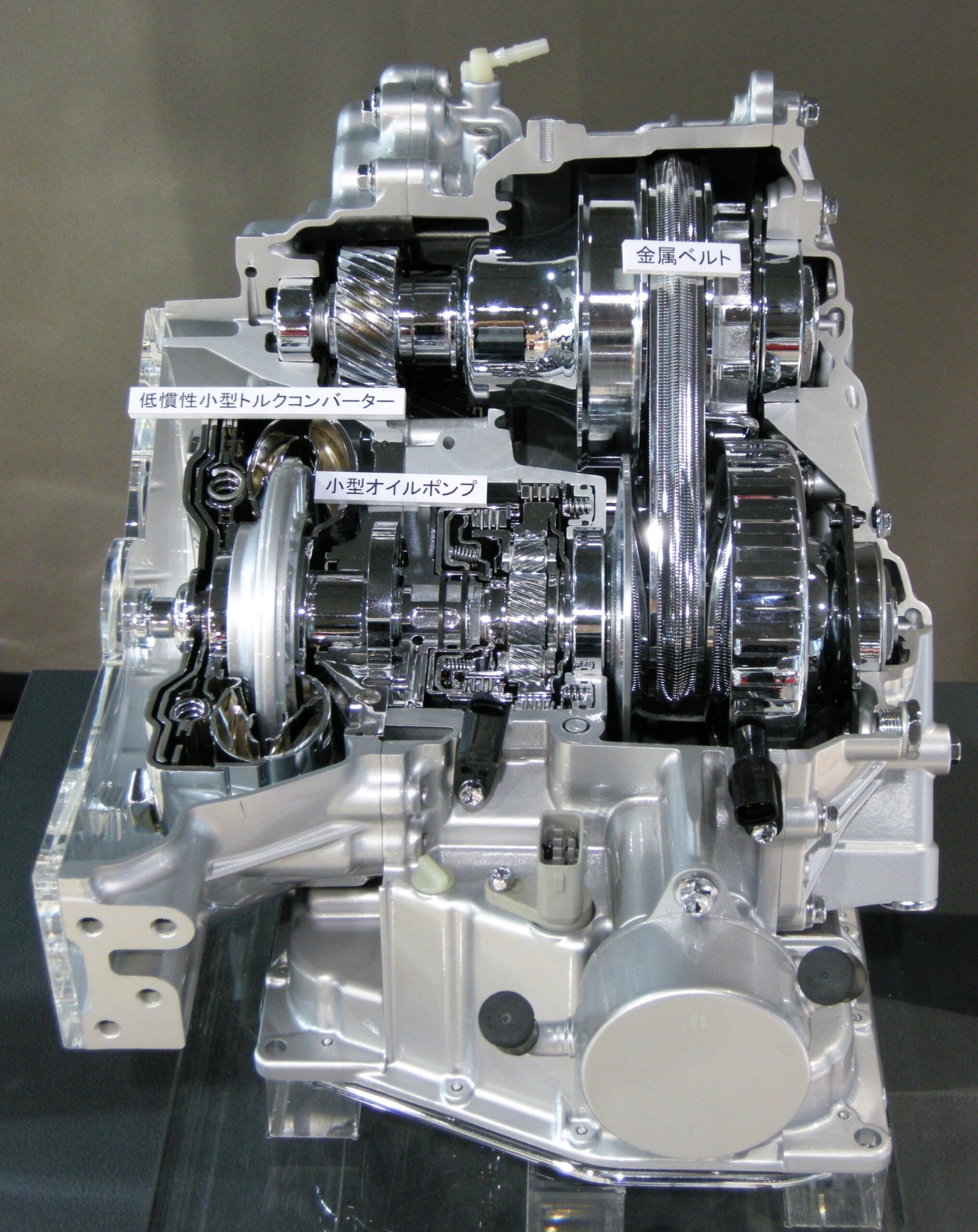
What is a Continuously Variable Transmission?
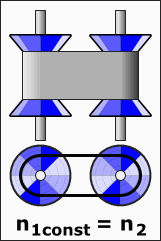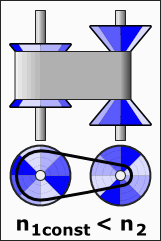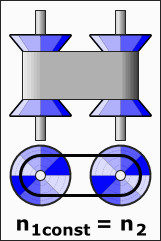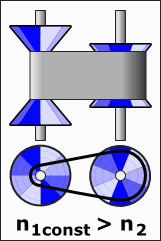
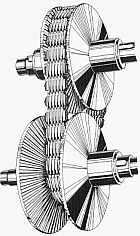
A continuously variable transmission (CVT) is a type of automated transmission that provides an endless range of gear ratios. Unlike traditional transmissions, which operate with a fixed number of gear ratios, a CVT can seamlessly change through varying gear ratios, ensuring a smoother drive. This flexibility enables the engine to maintain a consistent angular velocity while allowing the vehicle to adjust to different speeds.
Applications of CVTs
CVTs are popular in a range of vehicles and equipment, including cars, tractors, side-by-sides, motor scooters, snowmobiles, bicycles, and earthmoving machinery. The adaptability of a CVT makes it an appealing choice for various applications. For instance, the design often utilizes two pulleys that are connected by a belt or chain, facilitating this unique operation.
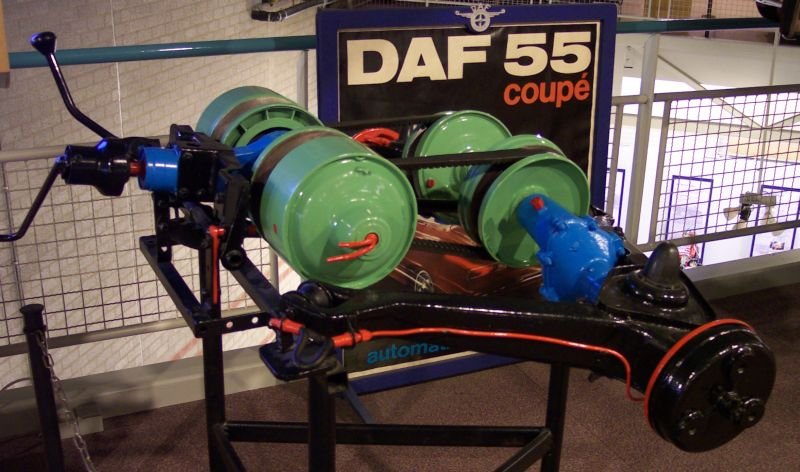
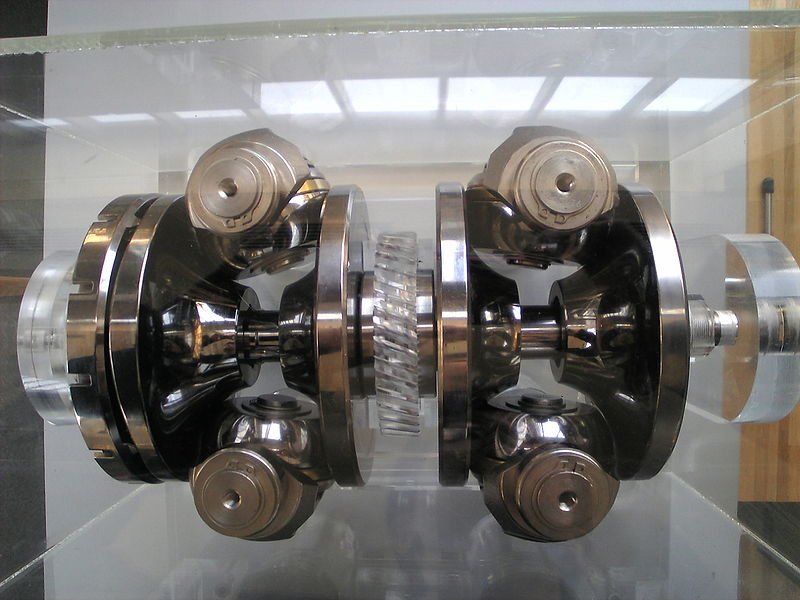



Advantages of a CVT
The primary advantage of a continuously variable transmission is its ability to optimize engine performance. By allowing the engine to operate at its most efficient RPMs, a CVT can enhance fuel economy, making it an efficient option for drivers concerned about carbon footprints and fuel costs. Additionally, CVTs tend to offer a smoother driving experience, as there are no distinct gear shifts that can interrupt acceleration.
-
Best Portable Tire Inflators
When it comes to roadside emergencies, having a reliable portable tire inflator can make all the difference. Not only can these compact devices save you from being stranded with a flat tire, but they can Read more…
-
How to Change Your Car’s Oil Like a Pro
Changing your car’s oil is a fundamental DIY maintenance task that can save you money and extend the life of your vehicle. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you perform an oil change like a Read more…
-
Types of Car Transmissions: Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVTs)
What is a Continuously Variable Transmission? A continuously variable transmission (CVT) is a type of automated transmission that provides an endless range of gear ratios. Unlike traditional transmissions, which operate with a fixed number of Read more…





0 Comments